Chapter:Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
Topics:Amines
- Derivatives of ammonia
- Obtained by the replacement of one, two or all the three H-atoms of ammonia by alkyl and/or aryl groups
- Example:
Structure of Amines
- Nitrogen on amines is sp3 hybridised.
- Geometry − Pyramidal
- Example: Pyramidal shapes of trimethylamine
- Bond angle C−N−E (E is C or H) is less than 109.5° due to the presence of unshared pair of electrons. It is 108° in the case of trimethylamine.
Classification
- Classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°)
- If one H-atom of NH3 is replaced by R or Ar, RNH2 or ArNH2 is obtained (primary amine, 1°).
- If two H-atoms of NH3 or one H-atom of RNH2 are replaced by alkyl or aryl group (R′), R2NH is obtained (secondary amine, 2°).
- On the replacement of another hydrogen atom by alkyl or aryl group, R3N is obtained (tertiary amine, 3°).
Nomenclature
Common System
- Aliphatic amine: Named by prefixing alkyl group to amine, i.e., alkylamine.
- Example: Methylamine (CH3NH2)
- Secondary and tertiary amines: Prefix di- or tri- is appended before the name of alkyl group when two or more groups are the same.
IUPAC System
- Named as alkanamines; derived by replacing the ‘e’ of alkane with the word amine.
- Example:
CH3NH2 − Methanamine
CH3CH2NH2 − Ethanamine
- When more than one amino group is present −
- Suitable prefix such as di-, tri-, etc., is attached to amine.
- ‘e’ of the suffix of hydrocarbon is retained.
- Positions of −NH2 group are specified by giving numbers to the parent chain.
- Example:
Ethane-1, 2-diamine
- For aryl amines −
- −NH2 group is directly attached to the benzene ring
- Simplest arylamine: C6H5NH2 (Common name − aniline, IUPAC name − benzenamine)
- While naming arylbenzenes by IUPAC system, the suffix ‘e’ of arene is replaced by ‘amine’.
- Common and IUPAC names of some alkylamine and arylamines are given in the table.
Amine
|
Common name
|
IUPAC name
|
CH3−CH2−NH2
|
Ethylamine
|
Ethanamine
|
Isopropylamine
|
Propan-2-amine
| |
Ethylmethylamine
|
N-Methylethanamine
| |
Trimethylamine
|
N,N-Dimethylmethanamine
| |
Aniline
|
Aniline or Benzenamine
| |
o-Toluidine
|
2-Aminotoluene
| |
N,N-Dimethylaniline
|
N,N-Dimethylbenzenamine
|
Topics:Methods of Preparation of Amines
Reduction of Nitro Compounds
- By passing H2 gas in presence of finely divided Ni, Pd, or Pt
Example:
- By reduction with metals in acidic medium
Ammonolysis of Alkyl Halides
- The carbon−halogen (C−X) bond in alkyl or benzyl halides can be easily cleaved by a nucleophile.
- The process of cleavage of C−X bond by ammonia molecule is called ammonolysis.
- The reaction is carried out in a sealed tube at 373 K.
- An alkyl or benzyl halide reacts with an ethanolic solution of NH3 as follows.
- Primary amine obtained behaves as a nucleophile and further reacts as
- Order of reactivity of halides with amines − RI > RBr > RCl
- Disadvantage − Mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salts is produced.
Reduction of Nitrites
- Reduction of nitrites with LiAlH4
- Catalytic hydrogenation of nitriles
Reduction of Amides
Gabriel Pthalimide Synthesis
- Used for the preparation of primary amine
- Reactions involved in the preparation of primary amine from phthalimide are as follows:
- Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by this process.
- Reason − Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation Reaction
- Preparation of primary amines by treating an amide with Br2 in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of NaOH
- Amine formed contains one carbon less than that present in the amide.
Topics:Physical Properties of Amines & Chemical Reaction of Amines – I
- Lower aliphatic amines are gases with fishy odour.
- Primary amines with three or more carbon atoms are liquid.
- Higher ones are solid.
- Aniline and other arylamines are colourless, but get coloured on storage due to atmospheric oxidation.
- Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water.
- Reason: Form H-bonds with water molecules
- Solubility decreases with increase in molar mass.
- Higher amines are insoluble in water.
- Amines are soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether and benzene.
- Order of boiling points of isomeric amines is
Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
Chemical Reactions
- Amines are basic in nature.
- Order of basicity of amines in the gaseous phase:
Tertiary amine > Secondary amine > Primary amine > NH3
- Order of basic strength in the case of methyl-substituted and ethyl-substituted amines is as follows:
- In the case of substituted aniline:
- Electron-releasing groups like −OCH3, −CH3 increase basic strength
- Electron-withdrawing groups such as −NO2, −SO3, −COOH, −X decrease basic strength.
- Alkylation
Amines undergo alkylation on reaction with alkyl halides.
- Sandmeyer’s reaction
- Acylation
Topics:Chemical Reactions of Amines – II
Carbylamine Reaction
- Known as carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test
- Used as a test for primary amines
- 2° and 3° amines do not show this test
Reaction with Nitrous Acid
HNO2is prepared in situfrom a mineral acid (HCl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
- Primary aliphatic amines
- Aromatic amines
- Secondary and tertiary amines react differently with HNO2.
Reaction with arylsulphonyl chloride
- Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) (known as Hinsberg’s reagent) reacts with 1° and 2° amines to form sulphonamides.
- With primary (1°) amine
- With secondary (2°) amine
- No reaction with tertiary (3°) amines
- This reaction is used for the distinction of 1°, 2° and 3° amines.
Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Aniline is a resonance hybrid of five structures.
- −NH2 group is a powerful ortho and para directing group.
- Bromination
- Electrophilic substitution reaction of aromatic amines is of very high reactivity − tends to occur both at ortho and para positions. To prepare monosubstituted aniline, −NH2 group is protected by acetylation with acetic anhydride; then the desired substitution is carried out, followed by hydrolysis.
Activating effect of −NHCOCH3is less than that of the amino group.
Reason − Lone pair is less available on nitrogen for donation to the benzene ring by resonance.
- Nitration
- In strong acidic medium, anilinium ion is formed, which is meta directing. Hence, significant amount of meta derivative is also formed along with ortho and para isomers.
- By protecting −NH2 group by acetylation reaction, para isomer can be obtained as the major product.
- Sulphonation
Topics:Diazonium Salts
- General formula =
R → An aryl group
X− ion →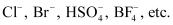
- Examples:
- Primary aliphatic amines form unstable alkyldiazonium salts.
Primary aromatic amines form stable arenediazonium salts, which are stable for a short time in solution (at 273 − 278 K).
- Stability of arenediazonium salts can be explained on the basis of resonance.
Preparation
- HNO2 is produced in the reaction by the reaction of NaNO2 and HCl.
- The conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts is called diazotisation.
Physical properties
- Colourless crystalline solid
- Readily soluble in water
- Stable in cold, but reacts with water when warmed
- Decomposes easily in dry state
- Benzenediazonium fluoroborate is water insoluble and stable at room temperature.
Chemical Reactions
Reaction Involving Displacement of Nitrogen
group is a good leaving group and escapes from the reaction mixture as a gas.
- Replacement by halide or cyanide ion
- Sandmeyer reaction
- Gatterman reaction
- Replacement by iodide ion
- Replacement by fluoride ion
- Replacement by Hydrogen atom
- Replacement by hydroxyl group
- Replacement by −NO2 group
Reactions Involving Retention of Diazo Group
- Coupling reactions
- Azo products are obtained, which have an extended conjugated system. Both the aromatic rings are joined through the −N=N− bond.
- It is an example of electrophilic substitution reaction.
Importance of Diazonium Salts in synthesis of aromatic compounds
- Substituted aromatic compounds can easily be prepared by the replacement of diazo group, which cannot be obtained by direct substitution in benzene or substituted benzene.
- − F, −Cl, −Br, −I, −CN, −OH, −ON2 groups can be introduced into the aromatic ring.
Topics:Nitro and Cyano Compounds
Cyano compounds
The organic compounds containing −CN as a functional group, are called cyano compounds.
Depending on the mode of attachment through the carbon or the nitrogen atom, they are classified as cyanide or isocyanide respectively.
As per IUPAC nomenclature, they are written with a suffix “nitrile”.
For example: CH3CN is ethanenitrile; and C2H5CN is propanenitrile.
Preparation of cyanides
- By heating alkyl halides with alcoholic potassium or sodium cyanide solution at about 100° C
- Industrial method: By distilling ammonium salt of a fatty acid with P2O5, SOCl2, POCl3 or alumina
- By dehydration of aldoximes with acetic anhydride or P2O5
- By reaction of Grignard reagent with cyanogens chloride
Properties of cyanides
- Cyanides can be represented as a resonance hybrid of two structures:
Thus, electrophilic attack takes place on N whereas nucleophilic attack takes place on C.
- In cyanides, the unshared electron pair is present on sp hybridised atom.So, they are less basic than ammonia.
- Both acidic and basic hydrolyses of cyanides result in the formation of carboxylic acids, with the evolution of ammonia.
- On reduction, the cyanides get converted to amines.
- Stephen’s reaction:
- Reaction with Grignard reagent and organolithium compounds:
Uses of cyanides
- Alkyl cyanides are used in the laboratory synthesis of organic compounds such as acids and amines.
- Acrylonitrile is used as an industrial solvent.
Preparation of alkyl isocyanides
- By heating alkyl halide with aqueous ethanolic solution of silver cyanide
- Carbylamine reaction:
- By the dehydration of N−alkyl formamide
Chemical properties of isocyanides
- The acidic hydrolysis of isocyanides yields primary amines.
Note:Alkyl isocyanides do not undergo basic hydrolysis because OH−ions are repelled by negatively charged carbon.
- Reduction:
- Action of heat:
Uses:
- Due to their characteristic unpleasant smell, alkyl isocyanides are used in detection of leakages.
- Carbylamine reaction is used for the detection of primary amino group.
Distinction between alkyl cyanides and alkyl isocyanides
Test
|
Ethyl cyanide
|
Ethyl isocyanide
| |
(1)
(2)
|
Odour
Boiling point
|
Strong but pleasant
98° C (High)
|
Extremely unpleasant
78° C (Low)
|
(2)
|
Dipole moment
|
High (≈ 4D)
|
Low (≈3D)
|
(3)
|
Solubility in water
|
Soluble
|
Only slightly soluble
|
(4)
|
Hydrolysis
|
Acidic and basic hydrolyses are possible
|
Only acidic hydrolysis is possible
|
(5)
|
Reduction
|
Yields 1° amine
|
Yields 2° amine
|
(7)
|
Action of heat
|
No effect
|
Formation of ethyl cyanide
|
Nitro compounds
Organic compounds containing −NO2 as a functional group are called nitro compounds. They may be aliphatic or aromatic.
Preparation
- From Alkyl Halides: Alkyl bromides and iodides (especially primary and secondary) react with silver nitrite in alcohol to give nitroalkanes as major alkyl nitrites as minor products.
Nitrite ion 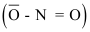 is an ambident nucleophile since it has two sites (oxygen and nitrogen) through which it can attack an alkyl halide. Attack through nitrogen results in nitro compounds while attack through oxygen results in nitrites. Alkali metal nitrites are ionic compounds; therefore,
is an ambident nucleophile since it has two sites (oxygen and nitrogen) through which it can attack an alkyl halide. Attack through nitrogen results in nitro compounds while attack through oxygen results in nitrites. Alkali metal nitrites are ionic compounds; therefore, attacks chiefly through oxygen, to form predominantly alkyl nitrites. In contrast, silver nitrite is a covalent compound, and hence, only nitrogen electrons are available for bond formation. As a result, silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds.
attacks chiefly through oxygen, to form predominantly alkyl nitrites. In contrast, silver nitrite is a covalent compound, and hence, only nitrogen electrons are available for bond formation. As a result, silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds.
- From Hydrocarbons: A mixture of conc. HNO3 and conc. H2SO4 reacts with benzene to give nitrobenzene.
Mechanism:
Step-I: Formation of nitronium ion:
This electrophilic substitution reaction occurs as the following two-step mechanism.
Step-II: Attack of nitronium ion onto the benzene ring
Step-III: Loss of proton to form nitrobenzene
Reaction of hydrocarbons with fuming HNO3
Physical properties of nitro compounds
- Odour: The nitroalkanes are colourless and pleasant smelling liquids.
Aromatic nitro compounds are either pale yellow liquids or solids with distinct smells.
For example, nitrobenzene is a pale yellow liquid having the odour of bitter almonds.
- Boiling point: The nitroalkanes and nitroarenes are highly polar compounds. As a result, they have a much higher boiling point than other hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Further, nitroalkanes also have a much higher boiling point than the less polar isomeric alkyl nitrites.
- Solubility: Nitroalkanes are sparingly soluble in water while nitroarenes are insoluble. However, both nitroalkanes and nitroarenes are readily soluble in organic solvents.
- Stability: Most of the nitroalkanes are quite stable and hence can be distilled without decomposition under atmospheric pressure. In contrast, isomeric alkyl nitrites explode on heating.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Some important chemical reactions of nitro compounds are:
- Reduction
- Hydrolysis
- Action with nitrous acid
- Tautomerism
- Acidic character
- Halogenation
- Ring substitution reactions of nitrobenzene
1. Reduction
Reduction of nitro compound to primary amine
On the basis of pH of the reaction medium and nature of the reducing agent, the final product may differ.
(a) Reduction in the Acidic Medium
Both aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds can be reduced to the corresponding primary amines in the presence of Zn, Fe or Sn and conc. HCl.
The intermediate products, nitroso compounds and hydroxylamines, are transitory and are reduced as soon as they are formed.
b) Reduction in the Neutral Medium.
In the neutral medium (Zn dust and NH4 Cl solution), both aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds are reduced to the corresponding hydroxylamines.
These hydroxylamines reduce the Tollen’s reagent to metallic silver. This reaction is used as a test for nitro compounds (Baker-Mulliken’s test).
c) Reduction in the Alkaline Medium
The reduction of the aromatic nitro compounds in the alkaline medium gives out different (bimolecular reduction) products depending upon the nature of the reducing agent employed. For example,
(d) Catalytic Reduction
Both aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds can also be reduced to the corresponding primary amines with hydrogen, in the presence of Raney nickel, platinum or palladium as catalyst. For example,
(e) Reduction With Metal Hydrides.
Nitroalkanes are reduced to the corresponding primary amines with lithium aluminium hydride. For example,
Aromatic nitro compounds, on reduction, give azo compounds and not primary amines. For example,
(f) Electrolytic Reduction.
Electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in a weakly acidic medium gives aniline, but in a strongly acidic medium, gives p-aminophenol.
(g) Selective-Reduction
If two or more nitro groups are present in the benzene ring, it is possible to reduce one of them without affecting the other. Such reductions are called selective reductions. For example, reduction of m-dinitrobenzene with sodium or ammonium sulphide gives m -nitroaniline.
2. Hydrolysis
(a) Primary nitroalkanes, when treated with boiling 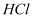 or 85 %
or 85 % 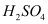 , undergo hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and the corresponding salt of the hydroxylamine.
, undergo hydrolysis to form carboxylic acid and the corresponding salt of the hydroxylamine.
This reaction is used for the manufacture of hydroxylamine.
(b) In contrast, secondary nitroalkanes, upon hydrolysis with boiling HCl, give a ketone and nitrous oxide.
(c) Tertiary nitroalkanes, however,do not generally undergo hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid.
Action of nitrous acid: Primary, secondary and tertiary nitroalkanes behave differently towards nitrous acid.
(a) Primary nitroalkanes react with nitrous acid to form nitrolic acids which dissolve in alkalies to form a red solution.
(b) Secondary nitroalkanes react with nitrous acid to form blue coloured pseudonitroles which do not dissolve in alkali.
(c) Tertiary nitroalkanes do not react with nitrous acid since they do not have 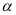 hydrogen atoms.
hydrogen atoms.
4. Tautomerism: Nitroalkanes containing 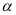 -hydrogen atoms, i.e., primary and secondary nitroalkanes, show tautomerism. For example, nitromethane exists in two tautomeric forms which are shown below.
-hydrogen atoms, i.e., primary and secondary nitroalkanes, show tautomerism. For example, nitromethane exists in two tautomeric forms which are shown below.
5. Acidic Character: The 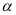 -hydrogen atoms of primary and secondary nitroalkanes are weakly acidic, and thus, can be abstracted by strong alkalies such as aqueous NaOH. Therefore, 1° and 2° nitroalkanes in aqueous NaOH form salts.
-hydrogen atoms of primary and secondary nitroalkanes are weakly acidic, and thus, can be abstracted by strong alkalies such as aqueous NaOH. Therefore, 1° and 2° nitroalkanes in aqueous NaOH form salts.
The main reasons for the acidic nature of 1o and 2o nitroalkanes are:
- strong electron-withdrawing inductive effect of the nitrogroup
- resonance stabilization of the carbanion formed after the removal of a proton
6. Halogenation: Primary and secondary nitroalkanes form halonitriles on recating with halogens. During this reaction, all the 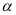 -hydrogen atoms of nitroalkanes are successively replaced by the halogen atoms. For example,
-hydrogen atoms of nitroalkanes are successively replaced by the halogen atoms. For example,
Chloropicrin is an important insecticide.
7. Ring Substitution Reactions of Nitrobenzene
(a) Electrophillic Substitution Reactions: Since the 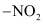 group is strongly ring deactivating, the incoming electrophile is directed towards meta position. This can be well understood with the help of the resonating structures.
group is strongly ring deactivating, the incoming electrophile is directed towards meta position. This can be well understood with the help of the resonating structures.
From the resonating structures, it is evident that because of its electron-withdrawing nature, nitro group reduces electron density more at o-and p-positions than at m-position. In other words, electron density is comparatively higher at m-position than at o-and p- positions.
Following are the electrophilic substitution reactions of nitrobenzene.
Note: Nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(b) Nucleophillic Substitution Reaction.
The presence of the positive charge at o- and p-positions in resonance structures suggests that nitrobenzene can also undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions at these positions. These reactions, however, occur with strong nucleophiles under drastic conditions. For example, nitrobenzene when fused with solid KOH gives a low yield of a mixture of o-and p- nitrophenols. The following chemical reaction takes place.
These are called as Hydrocarbons and if nitrogen is included as a likely basic of these molecular, pyridoxine tripalmitate manufacturer, many more potentials arise. Though most of the nitrogen-containing mixes have no commercial value yet some are useful.
ReplyDelete